Our Own Google PageSpeed Insights Score
This screenshot is from our live site on Google PageSpeed Insights. We optimize for fast Core Web Vitals on every release, and we do not compromise with speed.
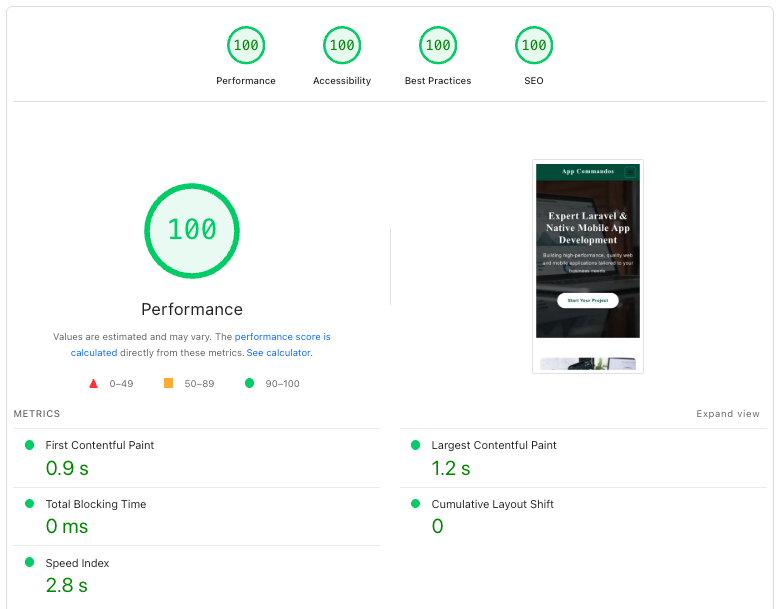
Source: Google PageSpeed Insights audit capture for appcommandos.com.
Why Performance Matters
Application performance directly impacts user experience, conversion rates, and search engine rankings. Studies show that users expect pages to load in under 3 seconds, and every additional second of load time can decrease conversions by 7%. Performance optimization is crucial for business success.
Performance optimization involves improving various metrics including page load time, time to first byte (TTFB), first contentful paint (FCP), largest contentful paint (LCP), and cumulative layout shift (CLS). These metrics affect both user experience and search engine rankings.
Web Performance Optimization
Web applications require optimization at multiple levels:
Frontend Optimization
Minify and compress CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files. Use code splitting to load only necessary code. Implement lazy loading for images and defer non-critical JavaScript. Optimize images with modern formats like WebP.
Backend Optimization
Optimize database queries with proper indexing and query optimization. Implement caching strategies using Redis or Memcached. Use connection pooling and optimize server response times. Implement API response compression.
CDN Implementation
Content Delivery Networks distribute content across multiple servers worldwide. They reduce latency by serving content from locations closest to users. CDNs cache static assets and reduce origin server load.
Browser Caching
Set appropriate cache headers to allow browsers to store static resources. This reduces server requests and improves repeat visit performance. Use cache busting for updated resources.
Database Optimization
Create proper indexes on frequently queried columns. Normalize database structure to reduce redundancy. Use query optimization techniques and consider read replicas for scaling read operations.
Server Configuration
Optimize web server settings like keep-alive connections, compression, and HTTP/2 support. Configure proper timeout values and connection limits. Use load balancers for distributing traffic.
Mobile App Performance
Mobile applications have unique performance considerations:
Battery Optimization
Minimize background processing and network requests. Use efficient algorithms and data structures. Implement proper lifecycle management to pause operations when apps are in background.
Memory Management
Properly manage memory to prevent leaks and crashes. Use efficient data structures and avoid retaining unnecessary objects. Implement proper cleanup in lifecycle methods.
Network Efficiency
Implement request batching and caching. Use compression for API responses. Minimize data transfer with efficient data formats. Implement offline capabilities to reduce network dependency.
Rendering Performance
Optimize UI rendering with efficient layouts and view recycling. Minimize overdraw and use hardware acceleration. Implement smooth animations with proper frame rates (60 FPS).
App Size Optimization
Reduce app bundle size by removing unused code and resources. Use ProGuard or R8 for code shrinking. Implement dynamic feature delivery for optional features.
Startup Time
Optimize app launch time by deferring non-critical initialization. Use lazy loading for heavy components. Minimize work on the main thread during startup.
Performance Monitoring
Continuous monitoring is essential for maintaining optimal performance:

Real User Monitoring (RUM): Track actual user experiences to identify performance issues. Tools like Google Analytics, New Relic, and Datadog provide insights into real-world performance metrics.
Synthetic Monitoring: Use automated tests to monitor application performance from various locations. This helps identify issues before users experience them.
Application Performance Monitoring (APM): Monitor server-side performance including response times, error rates, and resource utilization. APM tools help identify bottlenecks in application code and infrastructure.
Core Web Vitals: Google's Core Web Vitals measure loading performance (LCP), interactivity (FID), and visual stability (CLS). These metrics directly impact search rankings and user experience.
Performance Optimization Techniques
Key techniques for improving application performance:
- Lazy Loading: Load resources only when needed, reducing initial load time
- Code Splitting: Split JavaScript bundles to load only necessary code for each page
- Image Optimization: Use appropriate formats, compression, and responsive images
- Caching Strategies: Implement browser caching, CDN caching, and application-level caching
- Database Indexing: Create indexes on frequently queried columns to speed up queries
- Query Optimization: Write efficient queries, avoid N+1 problems, and use eager loading
- Minification: Remove whitespace and comments from code files
- Compression: Use Gzip or Brotli compression for text-based resources
- HTTP/2: Use HTTP/2 for multiplexing and server push capabilities
- Async Operations: Use asynchronous processing for time-consuming tasks
Performance Testing
Regular performance testing ensures applications meet performance requirements:
Load Testing: Test applications under expected load conditions to ensure they can handle traffic spikes.
Stress Testing: Push applications beyond normal capacity to identify breaking points and failure modes.
Endurance Testing: Run applications under normal load for extended periods to identify memory leaks and resource issues.
Spike Testing: Test applications with sudden increases in load to ensure they can handle traffic spikes gracefully.
Volume Testing: Test with large amounts of data to ensure applications can handle database growth and data processing requirements.